Video
Consultation

عربى

Video
Consultation

Book An
Appointment

Accident & Emergency
99616 30000
Help Desk
99616 40000

Robotic
Surgery

Patients Login Portal
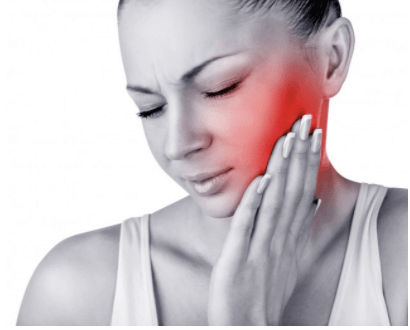
Learn more about trigeminal neuralgia, that is sudden, severe facial pain often described as the most excruciating pain known to humanity.
What is Trigeminal neuralgia?
Trigeminal neuralgia is a neurological condition characterised by severe facial pain that lasts for a few seconds to minutes. Since sensations from the face are carried by the trigeminal nerve to the brain, even mild stimulation on the face such as brushing your teeth or putting on makeup may trigger an attack of pain. TN typically affects one side of the face and in most cases, it’s the lower part of the jaw or teeth region.
What causes trigeminal neuralgia?
Trigeminal neuralgia is usually caused by the compression of the trigeminal nerve by a blood vessel, tumor, or a clump of arteries and veins. This compression causes the nerve to wear off its protective coating and as a result, one experiences flashes of excruciating pain when doing certain activities.
The trigeminal nerve is the fifth cranial nerve of the twelve and the largest. It is the primary sensory nerve of the head that transmits sensations of pain and touch from your face, teeth and mouth to the brain.
Diagnosis
Neurologists typically make diagnosis of this condition after ruling out other causes of pain. Treatment options vary depending upon the cause and severity and followingly patient may be asked to undergo CT scan or MRI of brain.
Treatment
1- Oral Medicine
An anticonvulsant medicine called carbamazepine or similar group medicine is the first treatment usually recommended to treat trigeminal neuralgia. Carbamazepine can relieve nerve pain by slowing down electrical impulses in the nerves and reducing their ability to transmit pain messages.
2- Neuro – Surgery
Microvascular decompression (MVD)
MVD is a major procedure that involves opening the skull and is carried out under general anesthetic by a neurosurgeon. Here, the surgeon relieves pressure on the trigeminal nerve from adjacent blood vessels by putting a sponge in between.
Many people find this surgery effective at easing or completely stopping the pain of trigeminal neuralgia. It provides the longest-lasting relief. However, some studies also suggest that the pain returns in about 3 out of 10 cases within 10 to 20 years of surgery.
At Present, MVD is the closest possible cure for trigeminal neuralgia. However, it is an invasive procedure and carries a risk of potentially serious complications, such as facial numbness, hearing loss or stroke.
3- Percutaneous procedures
Patients who don't want surgery or may not be fit to undergo surgery may be offered a little less invasive procedure.
Using X-ray or CT guidance, a thin needle or tube will be inserted from the cheek to the trigeminal nerve at the skull base. The procedure is carried out using various methods. Since the trigeminal nerve at skull base is damaged, it will not carry pain sensation.
The procedure can be achieved by
• Glycerol injection
• Radiofrequency lesioning - by using heat
• Balloon compression – where a tiny balloon inserted through the cheeks will be passed along a thin tube. The balloon is then inflated around the nerve to squeeze it and followingly removed.
Figure: Using CT guidance, a needle is inserted into the left trigeminal nerve followed by a glycerol injection.
Overall, these procedures are similarly effective in relieving trigeminal neuralgia pain, although there can be complications with each. It varies depending on the procedure and the individual.
The pain relief will usually last a few years or, in some cases, a few months. Sometimes these procedures may not work at all.A major side effect of these procedures is numbness either in one part or all of one side of the face, which can vary from being very numb or just pins and needles.
4 – Stereotactic Radiosurgery (Radiation)
Stereotactic radiosurgery is a fairly new treatment that uses a concentrated beam of radiation to deliberately damage the trigeminal nerve where it enters the brain.
Stereotactic radiosurgery does not require a general anesthetic and no cuts (incisions) are made in your cheek.
A metal frame is attached to your head with 4 pins inserted around your scalp and a local anesthetic is used to numb the areas where these are inserted.
Your head, including the frame, is then held in a large machine for 1 to 2 hours while the radiation is given. Followingly, the frame and pins will then be removed, and you will be able to leave home after a short rest.
The surgery may take a few weeks or sometimes many months to exhibit any changes but it can offer relief over the pain. For some people, it may take several months or years to show up visible changes.
The most common side effect of this surgery is facial numbness and pins and needles in the face.
At VPS Lakeshore, we offer consultation, diagnosis with advanced 3T MRI and treatment (medicine, neurosurgery and percutaneous glycerol injection).